NPTEL Computer Networks And Internet Protocol Week 1 And 2 Assignment Answers 2025
1. How many collision domains are in a 10-port hub, an 8-port switch (L2), and a 4-port router, respectively?
A collision domain is the segment of a network where data packets can collide.
a) 1, 8, and 4, respectively.
b) 10, 8, and 4, respectively.
c) 10, 10, and 10, respectively.
d) 5, 4, and 2, respectively.
✅ Answer: a
📝 Explanation:
- A hub has 1 collision domain (it broadcasts data to all ports).
- A switch (L2) creates separate collision domains per port → 8.
- A router creates 1 collision domain per port → 4.
2. Map the devices with their associated layer in the TCP/IP model.
A. NIC
B. Router
C. Bridge
D. Hub
a) A-2, B-3, C-2, and D-1
b) A-3, B-3, C-2, and D-1
c) A-3, B-3, C-1, and D-2
d) A-2, B-3, C-2, and D-2
✅ Answer: a
📝 Explanation:
- NIC → Data Link Layer (2)
- Router → Network Layer (3)
- Bridge → Data Link Layer (2)
- Hub → Physical Layer (1)
3. (Question text missing)
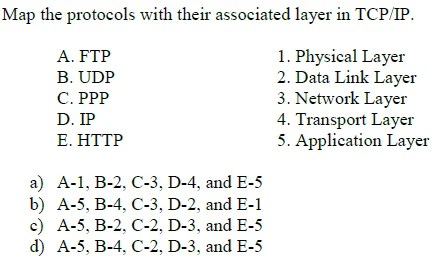
✅ Answer: d
4. Which of the following statements are concerned with encapsulation in computer networks?
I. It involves an addition of a header and trailer to the actual data as it moves down in the TCP/IP protocol stack.
II. At the transport layer, encapsulation includes port numbers and at the network layer, encapsulation includes IP addresses.
a) Only (I)
b) Only (II)
c) Both (I) and (II)
d) Neither (I) nor (II)
✅ Answer: c
📝 Explanation:
Encapsulation adds headers (and trailers) at each layer.
- Transport layer adds port numbers.
- Network layer adds IP addresses.
5. Which of the following is NOT a disadvantage of circuit switching over packet switching?
a) Delay in the establishment of a dedicated connection
b) Inefficient utilization of resources
c) Less scalable
d) Provides a dedicated communication path between two end hosts
✅ Answer: d
📝 Explanation:
While (a), (b), and (c) are disadvantages, (d) is a benefit of circuit switching.
6. Choose the FALSE statement.
a) Bridges filter network traffic based on IP addresses.
b) Hubs share bandwidth among all attached devices.
c) Switch provides dedicated bandwidth for each LAN segment.
✅ Answer: a
📝 Explanation:
Bridges filter traffic based on MAC addresses, not IP addresses.
7. Which transport layer protocol will be chosen by an application that does not require any reliability?
a) TCP
b) UDP
✅ Answer: b
📝 Explanation:
UDP is connectionless and does not provide reliability, making it suitable for fast, real-time communication (e.g., streaming).
8. Telnet troubleshooting considerations
a) Telnet is more secure than SSH.
b) Telnet is advisable in local networks to avoid security risks.
c) Telnet encrypts traffic.
d) Telnet transmits data in plaintext.
✅ Answer: b, d
📝 Explanation:
- Telnet is insecure (plaintext transmission) and should be used only on local networks.
- SSH is the secure alternative.
9. Roles and responsibilities of the Network Interface Card (NIC)
I. Segments large data into smaller packets.
II. Converts digital data to analog signals.
a) Only (I)
b) Only (II)
c) Both (I) and (II)
d) Neither (I) nor (II)
✅ Answer: c
📝 Explanation:
- NIC segments data into frames for transmission.
- Also performs digital-to-analog conversion for network transmission (if needed).
10. INCORRECT statements related to Bridges and Switches (L2)
a) Switch is more suitable than a bridge for small enterprises.
b) Switches are full-duplex; bridges are half-duplex.
c) Switches broadcast to all ports; bridges to designated ports.
d) Both are equally important in modern networks.
✅ Answer: a, c, d
📝 Explanation:
- a is correct, not incorrect (so shouldn’t be listed).
- c is false: switches use MAC tables to forward, not broadcast.
- d is debatable; switches have mostly replaced bridges in modern networks.
NPTEL Computer Networks And Internet Protocol Week 2 Assignment Answers
1. What is the difference between a ‘domain’ and ‘zone’ in DNS?
a) Zone is a subset of a domain, and a domain can contain multiple zones.
b) Domain is a subset of a zone, and a zone can contain multiple domains.
c) Domain is a logical hierarchy, whereas a zone is a physical DNS server.
d) DNS zones must be physically separated from each other.
✅ Answer: a
📝 Explanation:
A zone is a portion of the domain name space that is managed by a particular DNS server. A domain can be divided into multiple zones, each managed separately.
2. What makes FTP more secure than TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol)?
a) TFTP lacks features like user authentication and secure data transfer mechanisms.
b) TFTP allows simultaneous connections without encryption.
c) TFTP uses TCP, which is inherently less secure than UDP
d) TFTP is designed for unreliable networks, making it inherently less secure.
✅ Answer: a
📝 Explanation:
TFTP does not support authentication or encryption. FTP supports login and uses TCP, providing a more secure method for transferring files.
3. In the HTTP architecture, which of the following best describes a Uniform Resource Locator (URL)?
a) A secure protocol for encrypting HTTP communication.
b) A client-side scripting language for web development.
c) A unique identifier for resources, including the protocol, hostname, and path
d) A header that allows caching of web pages for better performance.
✅ Answer: c
📝 Explanation:
A URL specifies the protocol, host, and resource location (like a file or webpage). For example: https://example.com/index.html
4. Which of the following statements about HTTP proxy servers is NOT true?
a) They can cache responses from web servers to improve performance.
b) They can filter requests based on predefined rules.
c) They only work with secure connections (HTTPS).
d) They act as intermediaries between clients and web servers.
✅ Answer: c
📝 Explanation:
HTTP proxies can handle both HTTP and HTTPS with configurations like SSL tunneling. So, saying they “only” work with HTTPS is false.
5. Which of the following is correct for statements P, Q, and R?
P: HTTP uses TCP port 80 for communication.
Q: TELNET transmits data in an encrypted format.
R: DNS can operate on both TCP and UDP.
a) Both P and R are False, Only Q is True
b) Both P and R are True, Q is False
c) Only Q is True
d) Only R is False
✅ Answer: b
📝 Explanation:
- P is True: HTTP uses port 80 (TCP).
- Q is False: TELNET sends data in plaintext.
- R is True: DNS uses UDP for queries, and TCP for zone transfers.
6. What is the correct syntax to be written in the command line to initiate a Telnet connection to the web server of www.iitkgp.ac.in?
a) telnet/www.iitkgp.ac.in
b) telnet:www.iitkgp.ac.in
c) telnet://www.iitkgp.ac.in
d) telnet www.iitkgp.ac.in
✅ Answer: d
📝 Explanation:
The correct CLI syntax is:
bashCopyEdittelnet www.iitkgp.ac.in
7. Which of the following protocols allow non-ASCII data to be sent over email?
a) IMAP4
b) TELNET
c) MIME
d) POP3
✅ Answer: c
📝 Explanation:
MIME (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) allows emails to include non-text (non-ASCII) content like images, audio, video, etc.
8. Which of the following is true about the mail transfer protocol?
S1: Can send image files with the help of IMAP4
S2: Can send image files with the help of POP3
S3: IMAP4 is more secure than POP3
a) Only S1
b) Only S2
c) S2 and S3 only
d) S3 Only
✅ Answer: d
📝 Explanation:
- S1 and S2 are False: Sending images is handled by MIME, not IMAP4 or POP3.
- S3 is True: IMAP4 is generally more secure and feature-rich than POP3.
9. (Missing Question)

✅ Answer: a
10. Consider the following statements:
S1: A user requests a web page with text and one image. The client sends 1 request and gets 4 responses.
S2: Two web pages cannot be sent over the same persistent connection.
a) Only S1 is true
b) Only S2 is false
c) Both S1 and S2 are true
d) Both S1 and S2 are false
✅ Answer: d
📝 Explanation:
- S1 is false: The browser sends separate requests for text and each image.
- S2 is false: HTTP/1.1+ supports persistent connections, allowing multiple requests over the same TCP connection.